Audio Codecs: From Common Choices to the Best Pick
Audio codecs play a vital role in modern digital communications and multimedia applications. Whether it is music streaming, video conferencing, or online education, audio codecs play a key role in ensuring audio quality and transmission efficiency. This article aims to explore common audio codecs, analyze their technical characteristics and application scenarios, and introduce the current best audio codecs and the relevant audio settings.

What is an audio codec?
An audio codec is an algorithm used to encode and decode digital audio signals. Its main function is to compress the original audio signal into a smaller data file for easy storage and transmission, while restoring the quality of the original audio as much as possible during decoding.
The audio encoding process includes steps such as sampling, quantization, and compression, which reduce the amount of data by removing redundant information and imperceptible audio components. The decoding process is the inverse of the encoding process, aiming to restore the original audio signal as much as possible.
Common audio codecs
MP3(MPEG-1 Audio Layer III)
MPEG Layer III is a general-purpose audio codec based on perceptual modeling that produces low bitrates without noticeable quality loss of the decoded audio signal. MPEG Layer III is standardized according to ISO/IEC. The MPEG Layer 3 bitstream format is commonly referred to as MP3. Its main advantages are its popularity and hardware support.
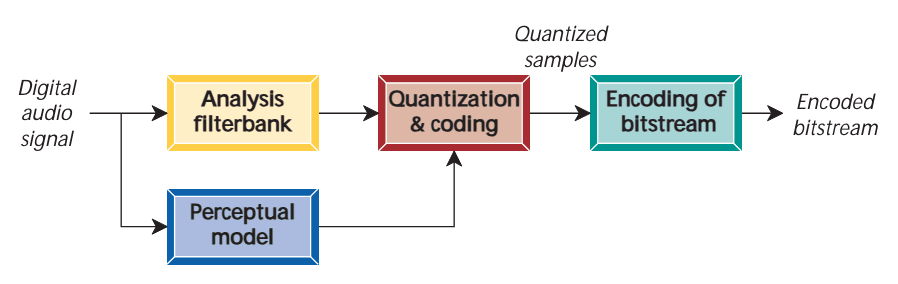
Before encoding, the audio signal needs to be preprocessed. This includes separating the stereo signal into left and right channels and dividing the audio signal into several frames, each of which usually contains 1152 samples.
The human ear's perception of sound, namely the psychoacoustic model, is used. By analyzing which parts of the audio signal are inaudible to the human ear, these parts can be removed to reduce the amount of data.
In order to better analyze the audio signal, the MP3 encoder converts the time domain signal into a frequency domain signal. This is usually achieved through fast Fourier transform (FFT, an efficient algorithm for computing discrete Fourier transform and its inverse transform) or modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT, or Modified Discrete Cosine Transform, is a transform technique used in audio and video coding and decoding).
In the frequency domain, the audio signal is quantized, that is, the continuous signal value is discretized. This step will introduce errors, but through the psychoacoustic model, the errors can be controlled within the acceptable range for the human ear. The quantized data is further compressed by lossless compression algorithms such as Huffman coding.
Finally, the encoded data is formatted into a bit stream. The bit stream includes a frame header, audio data, and auxiliary data. The frame header contains synchronization information and encoding parameters, the audio data is the compressed audio signal, and the auxiliary data is used for error correction and other purposes.
The first step of decoding is to parse the bitstream and extract the frame header and encoded audio data from it. The frame header is used to determine decoding parameters such as sampling rate and bit depth.
The parsed audio data needs to be inverse quantized, that is, the discretized signal value is restored to a continuous signal. This step will introduce some errors, but these errors are usually within the control range of the psychoacoustic model.
The inverse quantized data is still in the frequency domain and needs to be restored to the time domain through an inverse frequency domain transform (such as inverse MDCT).
Finally, the reconstructed time domain signal is reassembled into a stereo signal and output as audio data in PCM format.
AAC(Advanced Audio Coding)
At present, with the increasing demand for high-quality digital audio systems, the corresponding digital audio processing technology is also constantly improving. MPEG-1 Audio (ISO/IEC 11172–3) provides three different compression levels, namely Layer I, II and III. MP3 is the abbreviation of MPEG-1 Layer 3. It has been widely used in Internet audio and handheld devices. MPEG-2 Part 7 provides a new coding standard that is incompatible with MPEG-1 Audio. It is named AAC (Advanced Audio Coding). Its compression efficiency is 30% higher than that of MP3. AAC is widely used in streaming services such as Apple Music and YouTube. AAC has better sound quality than MP3 at lower bit rates and is widely used in streaming platforms and mobile devices.
Next, we will compare the differences between AAC and MP3 from the composition of the filter bank, the choice of window shape and the type of translation block.
1. In the composition of the filter bank, AAC only contains the standard MDCT. Compared with MP3, AAC does not have an analysis subband filter that divides the audio signal into 32 equal subbands. Therefore, the shortcomings of the analysis subband filter will not be brought into AAC, such as lossy transformation. It can be seen that the filter bank module in AAC is lossless, while the module in MP3 brings a small amount of distortion due to the introduction of the analysis subband filter.
2. In terms of the choice of window shape, AAC has Sine window(Is a simple window function whose main feature is to use a period of the sine function as the shape of the window function) and KDB window(Is an improved window function based on Kaiser window and is widely used in audio coding) to adapt to the different characteristics of audio signals, while MP3 only contains Sine window, and the flexibility of selection is not as good as AAC. Therefore, compared with MP3, AAC can choose different window shapes for different types of signals, so that distortion and coding efficiency can be better balanced.
3. In terms of the choice of block type, AAC has longer long blocks and shorter short blocks than MP3. Therefore, when long block coding is used, AAC has higher frequency resolution than MP3, which improves coding efficiency. When short block coding is used, AAC has higher time domain resolution than MP3, which controls the noise generated by quantization within a smaller time domain range. In summary, only in the filter module, AAC shows better coding efficiency and distortion control than MP3.
Opus
Opus is an open source audio codec developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), designed for interactive and real-time applications, providing excellent compression efficiency and audio quality, especially in low-latency environments. Opus performs particularly well at low bit rates and is suitable for VoIP and game audio.
Opus uses a hybrid coding architecture that combines the advantages of SILK and CELT. SILK is mainly used for speech coding, providing efficient speech compression and low latency; while CELT is used for music and high-fidelity audio, providing high-quality audio coding.
Opus supports bitrates from 6 kbps to 510 kbps, with sampling rates from 8 kHz to 48 kHz. While research using the Opus codec is limited, it has been shown to be comparable and, in some cases, provide better quality than many popular codecs at similar bitrates. Opus also allows for a wide range of frame sizes, from 2.5ms to 60ms.
FLAC(Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC is a lossless audio compression format that can reduce file size without losing any audio information. FLAC is mainly used for high-fidelity audio storage and transmission. FLAC is widely used among music lovers and audio archives.
Vorbis
Vorbis is an open source audio codec that provides good compression efficiency and audio quality and is commonly used in games and streaming applications. The main advantages of Vorbis are that it is open source and patent-free.
Comparison of common audio codecs
| AAC | MP3 | Opus | FLAC | Vorbis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression efficiency | Excellent | Lower | Provides excellent compression efficiency at low bit rates | Lossless compression, not suitable for low bandwidth environments | Provides good compression efficiency, but not as good as Opus |
| Audio Quality | High sound quality | Poor sound quality at low bitrates | Provides excellent sound quality at all bit rates, especially at low bit rates | Lossless sound quality for high-fidelity audio | Provides high sound quality, but not as good as Opus |
| Computational complexity | Moderate computational complexity, suitable for most applications | Low computational complexity, suitable for real-time applications | Computational complexity is high, but suitable for low-latency applications | The computational complexity is lower, but the file size is larger | Moderate computational complexity, suitable for most applications |
| Compatibility | Widely compatible, especially on mobile devices and streaming platforms | One of the most widely compatible codecs | Gradually adopted by more platforms, especially in real-time communication | Widely used in the hi-fi audio community, but less commonly in streaming | Widely used in the open source community, but not as popular as AAC and MP3 |
Advanced audio codecs
Soundstream
Soundstream is an end-to-end neural network audio codec that enables efficient compression while maintaining high sound quality. Its main feature is the use of deep learning technology for audio signal processing, which significantly improves coding efficiency and sound quality.
Audioec
Audiodec is an open source, high-fidelity neural network audio codec designed for real-time audio streaming. Audiodec is able to provide high-quality audio transmission with low latency and is suitable for a variety of real-time application scenarios.
Lyra
Lyra is a neural network-based low-bitrate audio codec developed by Google, designed for low-bitrate voice transmission. It is designed to provide high-quality voice transmission, maintaining good sound quality even under low bandwidth conditions. Combined with the open AV1 codec, voice chat can be achieved at a network speed of 56kbps. Lyra uses machine learning and other technologies for extremely low-bitrate voice compression, and can even work at a speed of 3kbps.
Lyra V2 uses the SoundStream end-to-end neural audio codec, has better performance than the Opus audio codec, improved audio quality, etc. The open source code of Lyra V2 is available today.
The best audio codecs in 2024
AAC is a lossy audio compression format designed to provide high-quality audio output with a smaller amount of data. It uses advanced perceptual coding technology to remove audio information that is imperceptible to the human ear, thereby achieving efficient compression.
AAC usually provides better sound quality than MP3, WMA and OGG at the same bit rate. Its advanced compression algorithm can significantly reduce the amount of data while maintaining sound quality.
In addition, AAC uses more advanced psychoacoustic models and transformation technology to provide high-fidelity audio output at lower bit rates.
And AAC has multiple variants, such as HE-AAC (High-Efficiency Advanced Audio Coding) and AAC-ELD (Enhanced Low Delay). HE-AAC provides higher sound quality at low bitrates, while AAC-ELD achieves low latency while maintaining high sound quality, suitable for video conferencing and real-time audio streaming.
AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) is one of the most popular and widely used audio codecs currently. It has significant advantages in audio quality and encoding efficiency, and is widely used in streaming services, mobile devices (including IOS and Android), broadcast (DAB+ and DVB), etc.
Related audio encoding settings
When using AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) for audio encoding, you can adjust various encoding settings according to specific application scenarios and needs to achieve the best sound quality and efficiency. Here are some common AAC encoding settings and their related descriptions:
Bitrate
Bitrate is a key parameter that affects sound quality and file size. Common bitrate settings include:
- Low bitrate (< 128 kbps): suitable for voice and low-quality music streaming.
- Medium bitrate (128-192 kbps): suitable for general music streaming and broadcasting.
- High bitrate (> 192 kbps): suitable for high-quality music storage and high-fidelity audio transmission.
Sample Rate
The sample rate determines the frequency range of the audio signal. Common sample rate settings include:
- 44.1 kHz: CD quality standard, suitable for most music and broadcasting.
- 48 kHz: widely used in video and professional audio applications.
- 96 kHz and above: used for high-resolution audio.
Encoding Mode
AAC supports multiple encoding modes:
- CBR (Constant Bit Rate): constant bit rate, suitable for real-time streaming and broadcasting.
- VBR (Variable Bit Rate): The bit rate is variable and dynamically adjusted according to the audio content. It is suitable for storage and download applications to obtain higher sound quality.
Channel Configuration
AAC supports multiple channel configurations:
- Mono: Suitable for voice and low-bandwidth applications.
- Stereo: Suitable for most music and video applications.
- Multi-channel (5.1, 7.1, etc.): Suitable for home theater and surround sound systems
Tencent MPS
Tencent MPS provides powerful audio processing capabilities, supporting various audio codecs such as AAC, MP3, Opus, and more. MPS can reduce bitrate by over 20% without compromising the original audio quality. Additionally, it enhances audio quality and improves user experience through various audio processing features such as noise cancellation, audio separation, volume equalization, and audio improvement.
You can explore the above features by experiencing the Demo. If you have further interest, please feel free to Contact Us.

