Understanding Variable Frame Rate: Improve Your Video Experience
In the ever-evolving world of digital media, video quality and efficiency are paramount. As technology advances, Variable Frame Rate (VFR) has emerged as a crucial technique in video encoding, offering significant benefits over traditional methods.
The Basics of Frame Rate
Frame rate, expressed in frames per second (fps), is fundamental to video technology. It represents the number of individual frames or images displayed each second during video playback or recording. Standard frame rates vary by the medium and intended effect, with 24 fps traditional for film, while 30 fps or 60 fps are common in television and online videos. The fixed frame rate, or Constant Frame Rate (CFR), has been the norm for decades, ensuring synchronization of audio with consistent video playback.
What is Constant Frame Rate (CFR)?
Constant Frame Rate (CFR) refers to the encoding technique where each frame in a video sequence is displayed at a consistent and unchanging rate. For example, a video set at 30 frames per second (fps) will maintain this rate throughout its entire duration, ensuring uniform time intervals between each frame.
In CFR, the video encoder processes and outputs frames at a fixed rate, regardless of the scene's complexity or motion. This fixed rate means that every second of the video contains the same number of frames, providing a steady and predictable playback experience.
What is Variable Frame Rate (VFR)?
Variable Frame Rate (VFR) is a technique used in video encoding where the frame rate of the video can change dynamically depending on the content being displayed. Unlike Constant Frame Rate (CFR), where each second of video has the same number of frames, VFR allows for a varying number of frames per second. This flexibility can lead to significant benefits in terms of storage efficiency and video quality.
In essence, VFR adjusts the frame rate on-the-fly, increasing it during scenes with a lot of motion and decreasing it during static scenes. This adaptability makes VFR particularly useful in scenarios where bandwidth and storage are limited, or where the content itself has varying levels of complexity.
The Difference Between CFR and VFR
The primary difference between Constant Frame Rate (CFR) and Variable Frame Rate (VFR) lies in the consistency of the number of frames displayed per second throughout the video.
Constant Frame Rate (CFR):
- Consistency: CFR maintains a fixed number of frames per second (fps) across the entire length of the video.
- Synchronization: With CFR, audio and video synchronization is typically easier to maintain because the timing is uniform.
- Compatibility: CFR is widely compatible with most video editing and playback systems.
- Predictability: Since the frame rate does not change, the size of the final video file and the required bandwidth for streaming are more predictable.
- Standardization: Many traditional broadcasting and DVD standards require CFR because of its stability and predictability.
Variable Frame Rate (VFR):
- Flexibility: VFR allows the frame rate to change dynamically throughout the video. It can increase for fast-moving scenes and decrease for static shots.
- Efficiency: VFR can be more efficient in terms of file size because it doesn't use a high frame rate when it’s not needed.
- Complexity: Handling VFR can be more complex, especially during editing and playback, because not all systems support the variable nature of the frame timing.
- Quality: For certain types of content, such as recorded gameplay or mixed-media presentations, VFR can maintain high visual quality without unnecessarily large file sizes.
- Potential Issues: VFR may cause issues with sync, especially if the software or hardware isn't designed to handle frame rate variability.
In essence, CFR is the more traditional and widely supported format that guarantees compatibility and ease of editing but can result in larger file sizes. VFR offers more efficient data storage and potentially enhanced viewing experiences but requires careful handling to avoid sync and compatibility issues.
Advantages of Variable Frame Rate
Storage Efficiency: One of the most significant advantages of Variable Frame Rate is its ability to reduce the data size of video files. By allocating more frames to motion-heavy scenes and fewer frames to static scenes, VFR efficiently uses storage space. This reduction in data size can be crucial for streaming services and applications that require efficient use of storage.
Enhanced Video Quality: VFR improves the fluidity and clarity of videos, especially in dynamic scenes. By adjusting the frame rate based on the content, VFR ensures that high-motion scenes are captured with more frames, resulting in smoother playback. This can be particularly beneficial for action-packed videos, sports broadcasts, and gaming streams.
Flexibility: Variable Frame Rate offers dynamic adjustment according to content needs. This flexibility allows for a more tailored approach to video encoding, ensuring that each scene is encoded with the optimal number of frames. This adaptability can lead to a better viewing experience for the end-user.
Application Scenarios of Variable Frame Rate
Live Streaming: In live streaming, conditions can change rapidly, such as variations in network bandwidth or scene complexity. VFR allows the encoder to adjust the frame rate dynamically, ensuring a smoother streaming experience by reducing buffering and maintaining video quality.
Screen Recording: VFR is also widely used in screen recording applications. Different operations and scenes on a computer screen may require various frame rates. For instance, a static desktop background may need fewer frames than a high-motion video game. VFR allows screen recording software to adjust the frame rate dynamically, resulting in smaller file sizes and better quality recordings.
Animation and Special Effects: In the world of animation and special effects, achieving optimal visual effects often requires varying frame rates. VFR enables animators and special effects artists to use higher frame rates for complex scenes and lower frame rates for simpler scenes. This flexibility can lead to more efficient workflows and higher-quality animations.
Gaming Videos: Gaming videos often feature sequences with varying levels of action and detail. VFR can handle these fluctuations more efficiently than a constant frame rate, providing better synchronization and quality during high-action scenes while conserving resources during slower moments.
Sports Broadcasting: Sports events feature rapid motion and varying levels of activity. VFR allows broadcasters to adjust the frame rate in real-time, ensuring that fast-paced action is captured smoothly without unnecessary resource usage during slower moments.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): In VR and AR, the frame rate needs to adapt to different levels of interaction and complexity within the immersive environment. VFR ensures a seamless and responsive experience by adjusting the frame rate according to the content's demands.
Surveillance and Security Cameras: Security cameras often use VFR to adapt to varying levels of activity in their field of view. This helps in conserving storage space and processing power by lowering the frame rate during periods of inactivity and increasing it during moments of high activity.
Challenges of Variable Frame Rate
Compatibility: One of the primary challenges of Variable Frame Rate is ensuring compatibility with various media players and editing software. Not all players and software support VFR, which can lead to playback issues or synchronization problems. Ensuring broad compatibility is essential for the widespread adoption of VFR.
Synchronization: Maintaining audio and video synchronization in VFR streams can be challenging. Since the frame rate is not constant, the timing of audio and video must be carefully managed to ensure they remain in sync. This requires sophisticated encoding and playback mechanisms.
Complexity: The encoding and decoding processes for VFR are more complex than for CFR. This complexity can lead to increased processing power requirements and potential issues during playback. Handling this complexity effectively is crucial for delivering a seamless viewing experience.
Detecting and Handling Variable Frame Rate
Detecting Variable Frame Rate
Detecting VFR in video content is crucial for ensuring proper synchronization and playback. Video editing software often includes a feature that alerts you to VFR content when it is imported. Furthermore, media tools like MediaInfo or Adobe Premiere Pro can analyze a video file and report whether it's encoded with Variable Frame Rate (VFR) or Constant Frame Rate (CFR).
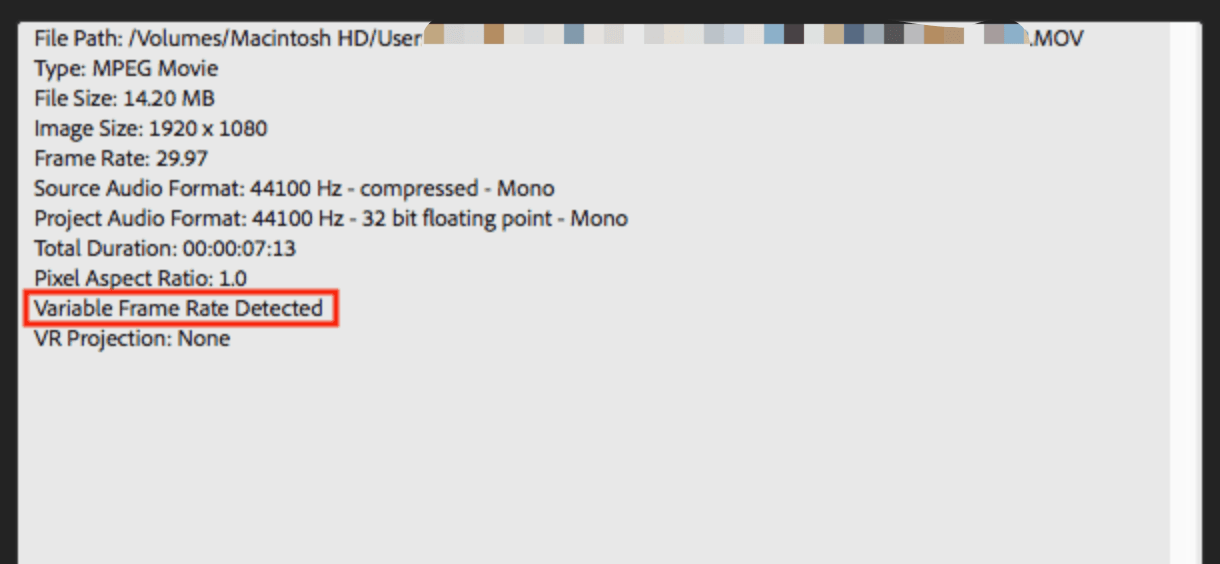
Handling Variable Frame Rate
Once VFR is detected, handling it properly is essential to maintain the integrity of audio-video synchronization and to ensure a smooth editing process.
Using VFR-Compatible Editing Software: Some modern video editing platforms like Adobe Premiere Pro are designed to handle VFR natively. They can automatically adjust the timeline to match the variable rates of the footage, preventing common issues like A/V desync.
Adjusting the Playback Engine: Some media players and editing systems allow customization of the playback engine settings to accommodate VFR content. Adjusting buffering and timing settings can ensure smoother playback.
Transcoding to Constant Frame Rate (CFR): If other methods are not suitable for you, you can try transcoding it to CFR. Transcoding software can convert VFR footage to a consistent CFR that matches the majority of editing and playback systems. This process safeguards against dropped frames and synchronization problems. However, this will result in the loss of the advantages of Variable Frame Rate (VFR).
Conclusion
Variable Frame Rate is a powerful technique that offers numerous benefits, including storage efficiency, enhanced video quality, and flexibility. Its applications span various industries, from live streaming to animation, making it a valuable tool for content creators and broadcasters.
However, VFR also presents challenges, including compatibility, synchronization, and complexity. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and adherence to best practices.
FAQs
Q: What is the primary difference between Variable Frame Rate (VFR) and Constant Frame Rate (CFR)?
A: The primary difference between Variable Frame Rate (VFR) and Constant Frame Rate (CFR) is that VFR allows the frame rate to change dynamically based on the content being displayed, while CFR maintains a consistent frame rate throughout the video. VFR adjusts the number of frames per second according to the complexity of the scene, leading to potential benefits in storage efficiency and video quality.
Q: How does Variable Frame Rate improve video quality?
A: Variable Frame Rate improves video quality by allocating more frames to high-motion scenes and fewer frames to static scenes. This dynamic adjustment ensures that fast-moving scenes are captured with greater detail and smoothness, resulting in enhanced fluidity and clarity. This adaptability makes VFR particularly beneficial for action-packed videos, sports broadcasts, and gaming streams.
Q: What are some common challenges associated with Variable Frame Rate?
A: Common challenges associated with Variable Frame Rate include compatibility with various media players and editing software, maintaining audio and video synchronization, and the increased complexity of encoding and decoding processes. Addressing these challenges requires sophisticated encoding techniques, robust error handling strategies, and adherence to best practices to ensure a seamless viewing experience.
You are welcome to Contact Us for more information.