FLV vs WebM vs MP4: See the Full Comparison
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, selecting the right video format is crucial for media distribution. With numerous options available, FLV, WebM, and MP4 stand out as popular choices. This article delves into their characteristics, comparing their technical aspects and highlighting the optimization advantages provided by Tencent MPS.
What is FLV?
FLV (Flash Video Format) is a container file format used to deliver digital video content over the internet using Adobe Flash Player or Adobe Air. Despite its previous popularity, its usage has declined with the decrease in support for Flash-based content.
What is WebM?
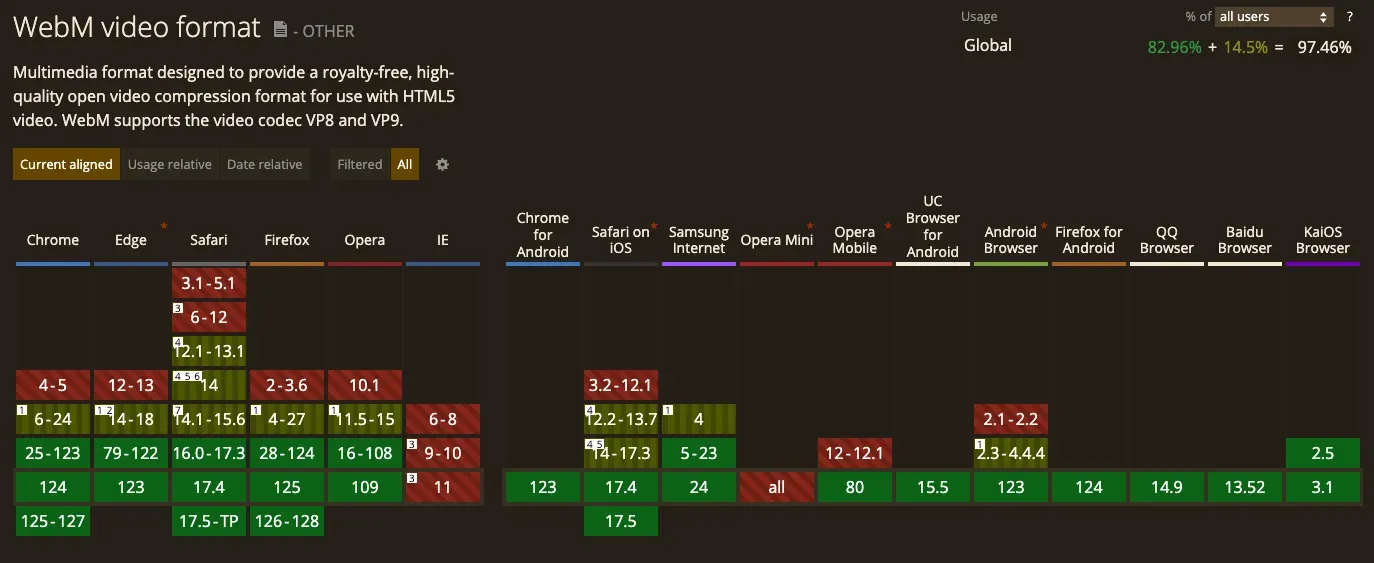
WebM is a video file format developed for the web by Google. It aims to provide high-quality video compression for use in HTML5 videos with the primary goal of delivering online video streaming with reduced bandwidth usage. WebM uses VP8 or VP9 video codecs, offering a fine balance between compression and quality.
What is MP4?
MP4, or MPEG-4 Part 14, is a digital multimedia container format most widely used across various platforms and devices. It stores not only video and audio but also subtitles and images. Renowned for its versatility, MP4 uses H.264 or H.265 video codecs, known for efficient compression without significantly compromising video quality.
Dissecting FLV, WebM and MP4: A Comparative Understanding
Here's a consolidated comparison table that captures the essential differences between FLV, WebM and MP4 formats:
| Feature | FLV | WebM | MP4 |
| Developed by | Adobe Systems | Moving Picture Experts Group | |
| File Extension | .flv | .webm | .mp4 |
| Video Codecs Supported | VP6, Sorenson | VP8, VP9 | H.264 (AVC), H.265 (HEVC) |
| Browsers and Platforms Supported | Limited, with decreasing support | Most major browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Opera) | Almost all browsers and platforms |
| Streaming Supported | Yes, but phasing out | Primarily for web streaming | Yes, versatile streaming capabilities |
| Devices Supported | Declining due to lack of Flash support | Constrained by browser compatibility | Broad compatibility across devices |
1. Compression Techniques and File Size
When it comes to compressing video data, both WebM and MP4 employ distinct methods that influence their end file sizes, a crucial factor for storage and streaming bandwidth.
FLV: Was known for its efficient streaming capabilities, albeit with larger file sizes compared to modern formats.
WebM: Utilizes the VP8 or VP9 video codec that significantly compresses video data, resulting in smaller file sizes without a drastic compromise in quality. This makes it exceptionally fit for web streaming purposes.
MP4: Leverages H.264 or H.265 codecs that are known for delivering a good balance between compression and quality. This ensures that videos are of a high enough quality for a variety of uses while still being reasonably sized.
2. Compatibility and Support Devices
The reach and compatibility of a video format can spell its success or demise.
FLV: FLV's compatibility has waned with the discontinuation of Flash support, making it less practical for current use. However, it is still feasible to play it using certain JavaScript libraries, like flv.js, allows for the playback of FLV files encoded with H.264 and AAC through the browser-supported Media Source Extensions.
WebM: Supported primarily by web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Opera. Its integration with HTML5 extends its compatibility to online platforms, albeit with limited support on some mobile and handheld devices.
MP4: Boasts near-universal support across not just web browsers but also on most hardware devices, including smartphones, tablets, gaming consoles, and more.

3. Video Quality and Encoding Efficiency
Quality retention in video codecs without bloating the file size is a hallmark of advanced video formats.
FLV: Lagged behind due to older compression standards.
WebM promises commendable quality, especially for videos streamed over the internet, thanks to efficient codecs like VP9 that offer good quality at lower bitrates.
MP4 edges out WebM slightly in this category due to the broader advancements and support in the H.264 and H.265 codecs, providing high-quality video even at reduced file sizes.
Optimization Advantages by Tencent MPS
Tencent MPS shines in optimizing video processing across both WebM and MP4 formats using cutting-edge technology.
Advanced Encoding Technology: MPS enhances video quality at lower bitrates remarkably, enabling premium streaming experiences without excessive data usage.
Ultra-High Definition Real-Time Transcoding: With its capability to support resolutions up to 8K and frame rates up to 144 FPS, Tencent MPS ensures videos are not only future-proof but visually stunning.
Optimized Transmission Efficiency: Achieves low-latency, stable cross-border transmissions, facilitating a seamless viewing experience for global audiences.
Cost-Effectiveness: By optimizing compression and streaming technologies, MPS significantly conserves on storage and bandwidth, enhancing resource efficiency.
Industry Recognition: The leadership of Tencent MPS in encoding technology is underscored by its accolades and adoption in the industry, marking its effectiveness in optimizing video codecs.
Conclusion
The exploration of FLV, WebM, and MP4 reveals a landscape marked by technological evolution and varied applicability. While FLV's era wanes, WebM and MP4 cater to the modern demand for efficient, high-quality video streaming. Tencent MPS emerges as a transformative force, optimizing these formats to meet the challenges of today's digital content distribution. Through innovative enhancements, MPS ensures that WebM and MP4 continue to deliver unparalleled video experiences, solidifying their relevance in the digital age.
To experience the best of Tencent MPS, request a free demo now! If you have any questions about our services, don't hesitate to Contact Us.
