AI Dubbing (excluding erasure) Integration
Last updated: 2025-12-16 17:49:02Download PDF
AI Dubbing Feature Overview
The AI dubbing feature can replace the original dubbing of a video with the AI-generated dubbing in the target language and embed the translated subtitles into the video images. To initiate an AI dubbing task, you need to use the following two files as input:
1. A clean video file with no subtitles in the source language on the video images.
2. A subtitle and speaker tag file (the Speaker file).
You can also directly call the Dubbing-Level Video Translation feature, input a video with original subtitles, and complete subtitle and dubbing translation in one stop to obtain a translated video.
Note:

Billing Instructions
When you initiate an AI dubbing task, you are charged for AI dubbing (cloned timbre) and subtitle embedding. Among them, subtitle embedding is optional.
Note:
The AI dubbing feature uses cloned timbre by default. The standard timbre capability is currently under upgrade and available only for beta testing. If you need to use the standard timbre, you can contact sales for support.
When you use the standard timbre, you are charged for AI dubbing (standard timbre) and subtitle embedding. Among them, subtitle embedding is optional.
Initiating a Video Translation Task
Pre-integration Prerequisites
Before integrating AI dubbing, you need to complete the following prerequisites for using Media Processing Service (MPS): Register and log in to a Tencent Cloud account, activate MPS, and grant permissions to service roles.
For detailed guidance, see Quick Start. For account authorization issues, see Account Authorization.
Method 1: Initiating a Task in the Console
1. Go to the Create a Task page in the console, specify the input file path, orchestration workflow, and output path in sequence.
2. In the orchestration configuration, select the Media AI - Intelligent Analysis node.
3. On the pop-up page on the right, select the preset template 32, enable Extended Parameters in the More Settings section, and then input the required parameters in ExtendedParameter based on Description of ExtendedParameter in the following section.
Note:
To initiate an AI dubbing task, you must input the subtitle file path or the Speaker file path in ExtendedParameter; otherwise, the task will fail.
The MPS console automatically escapes the JSON data. Input the data directly and do not input escaped strings. Otherwise, the task will fail.

Method 2: Initiating a Task by Calling an API
Call the ProcessMedia API, select the AiAnalysisTask task, set Definition to 32 (ID of the preset template), and fill in ExtendedParameter, which is the parameter that enables the AI Dubbing capability. For parameter values, see Description of ExtendedParameter in the following section. The JSON example for ProcessMedia is as follows:
{"InputInfo":{ //Input video path. Replace it with the path of your original video."Type":"URL","UrlInputInfo":{"Url":"https://test-1234567.cos.ap-nanjing.myqcloud.com/mps_test/myvideo.mp4"}},"OutputStorage":{ //Output Cloud Object Storage (COS) bucket. Replace it."Type":"COS","CosOutputStorage":{"Bucket":"test","Region":"ap-nanjing"}},"OutputDir":"/mps_test/output/",//Output folder path. Replace it."AiAnalysisTask":{"Definition":32, //Preset template ID. Enter 32."ExtendedParameter":"{\"dubbing\":{\"speakerUrl\":\"https://mycloud.com/path/to/file.json\"}}" //Required extension parameter. It is used to specify the speaker file path, subtitle style, and other parameters.},"TaskNotifyConfig":{ //Event callback notification configuration, which is optional."NotifyType":"URL","NotifyUrl":"http://www.qq.com/callback"}}
It is recommended that you use API Explorer for rapid verification. You can copy the above JSON data to the JSON mode in API Explorer, switch to the Form mode for automatic parsing, adjust required parameters such as input and output paths, and then click Initiate Call.
In API Explorer, the positions of ExtendedParameter in Form and JSON input modes are as follows:
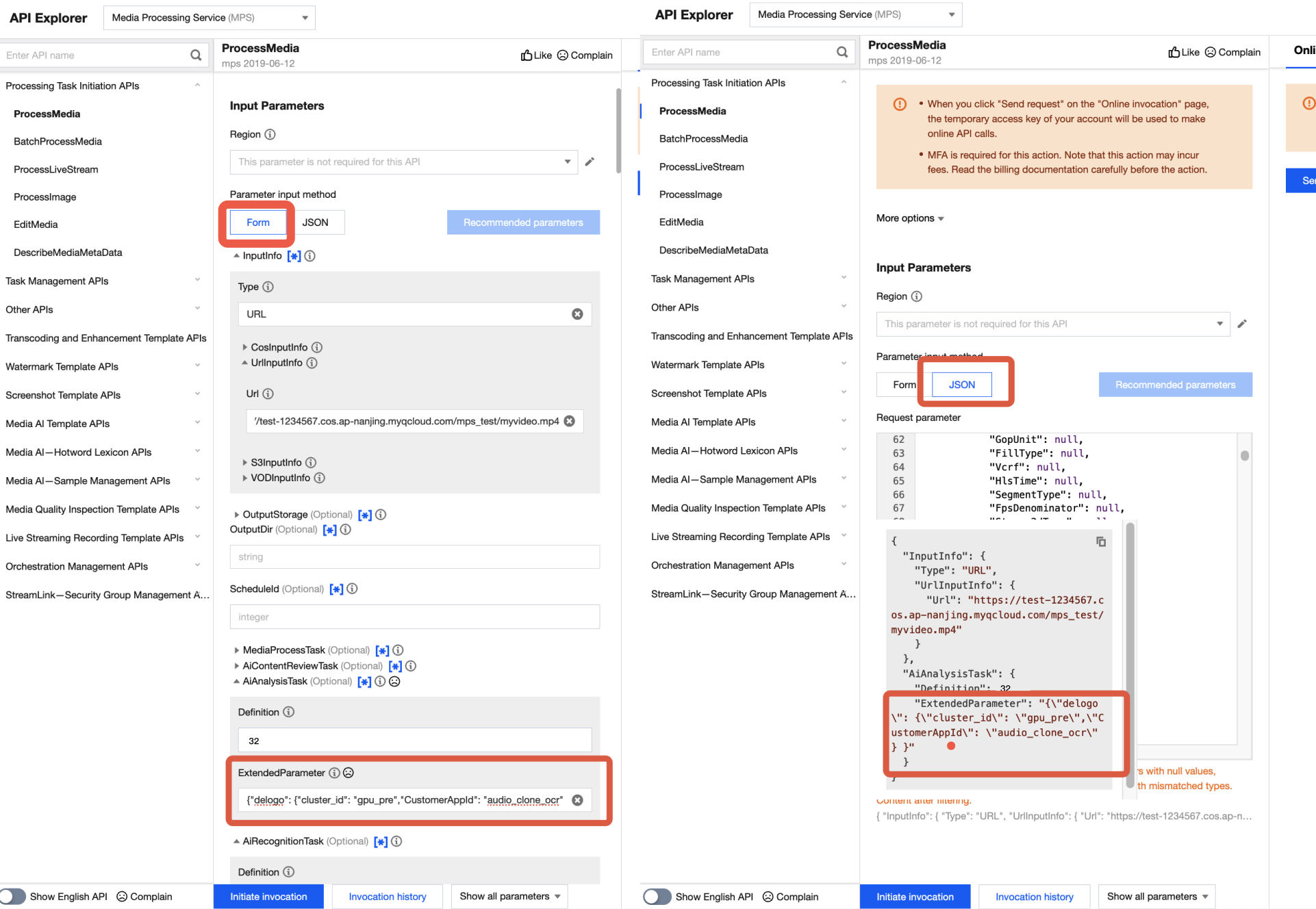
Note:
When you fill in values in the ExtendedParameter field in the Form mode of API Explorer, you need to directly input the JSON data instead of escaping it to a string. However, when you use the JSON mode of API Explorer or directly use the API, you should input an escaped string.
In the Form mode of API Explorer, input the JSON data in ExtendedParameter:
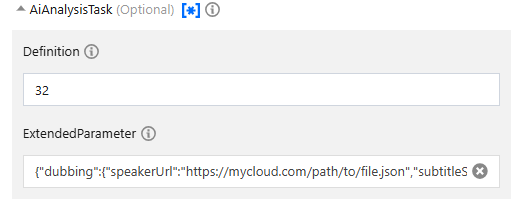
In the JSON mode of API Explorer, input an escaped string in the ExtendedParameter field. Example:
{\"dubbing\":{\"speakerUrl\":\"https://mycloud.com/path/to/file.json\"}}
Additional Notes
ExtendedParameter Description
ExtendedParameter is used for customizing settings of AI dubbing tasks. All optional parameters and their descriptions are as follows:Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
speakerUrl | string | 否 | Either Speaker File URL or Subtitle URLs must be provided. For details, please refer to the Speaker Data Format. |
srcLang | string | 否 | Source language. Optional when using speakerUrl mode. |
dstLangs | list<string> | 否 | Target dubbing languages. Optional when using speakerUrl mode. |
subtitleUrls | json | 否 | Input subtitle URLs. Either this or speakerUrl must be provided. |
subtitleUrls.srcSubtitleUrl | string | 否 | Original subtitle URL. |
subtitleUrls.dstSubtitleUrls | json | 否 | Target subtitle URLs, with language as key and subtitle URL as value. |
subtitle | json | 否 | Parameters related to output subtitles. |
subtitle.embed | bool | 否 | Whether to embed subtitles. Enabled by default. |
subtitle.style | json | 否 | Subtitle styling. Takes effect when subtitle embedding is enabled. |
subtitle.style.font | string | 否 | Font family. Uses default font when empty or set to "auto". For supported fonts, refer to SubtitleTemplate Data Structure. |
subtitle.style.fontSize | float | 否 | Font size. Default: 50 px. |
subtitle.style.marginV | float | 否 | Bottom margin. Default: 50 px. |
outputPattern | string | 否 | Output filename prefix. If not specified, defaults to "dub", with full filename as dub_{unixtime}.{format}. |
使用 speakerUrl 请求参数示例:
{"dubbing": {"speakerUrl": "https://mycloud.com/path/to/file.json", // Required. The Speaker file URL."subtitle": {"embed": true, // Specify whether to embed subtitles. true by default."style": { // The subtitle style. This parameter is valid only when subtitle embedding is enabled."font": "kai.ttf", // The font. Default value: "kai.tff"."fontSize": 50, // The font size. Default value: 50px."marginV": 50 // The bottom margin. Default value: 50.}},"outputPattern": "filename" // Optional. The prefix of the output file name.}}
使用 subtitleUrls 请求参数示例:
{"dubbing": {"srcLang": "zh","dstLangs": ["ja"],"subtitleUrls": {"srcSubtitleUrl": "https://test/zh.vtt", // Original-language subtitle URL."dstSubtitleUrls": {"ja": "https://test/ja.vtt" // Target-language subtitle URL.}},"subtitle": {"embed": true, // Specify whether to embed subtitles. true by default."style": { // The subtitle style. This parameter is valid only when subtitle embedding is enabled."font": "auto", // The font. auto means automatic matching based on subtitle language."fontSize": 0.04, // The font size. A value less than 1 represents a percentage."marginV": 0.15 // The bottom margin. A value less than 1 represents a percentage.}},"outputPattern": "filename" // Optional. The prefix of the output file name.}}
Note:
The duration of a single subtitle in the Speaker file or subtitle file must be no less than 0.15 seconds.
Speaker Files Description
Data Format
The Speaker file is a JSON-formatted file containing subtitles and corresponding speaker information. Its data format is as follows:
{"SrcLang": "zh","DstLangs": ["en"],"Speakers": [{"Id": "speaker_0","Gender": "male"},{"Id": "speaker_1","Gender": "female"}],"Clips": [{"TextStartTime": "00:00:00.100","TextEndTime": "00:00:00.600","SpeakerId": "speaker_0","SrcText": "没谁","DstTexts": {"en": "No one"}},{"TextStartTime": "00:00:01.0","TextEndTime": "00:00:01.200","SpeakerId": "speaker_1","SrcText": "早上好""DstTexts": {"en": "Morning"}}]}
Parameter | Required | Type | Description |
SrcLang | Yes | string | |
DstLangs | Yes | list<string> | Target language for translation. Currently, only a single language can be selected. For details, see Supported Languages. |
Speakers[i].Id | Yes | string | Speaker ID. |
Speakers[i].Gender | Yes | string | Speaker gender. Valid values: male and female. |
Clips[i].TextStartTime | Yes | string | Start timestamp of the subtitle clip. Format: hh:mm:ss.ms. |
Clips[i].TextEndTime | Yes | string | End timestamp of the subtitle clip. Format: hh:mm:ss.ms. |
Clips[i].SpeakerId | Yes | string | Speaker ID corresponding to the subtitle clip. |
Clips[i].SrcText | Yes | string | Source language of the subtitle slice. |
Clips[i].DstTexts | Yes | map<string,string> | Target language of the subtitle slice. Currently, only a single language can be selected. |
Speaker File Modification Examples
Modify incorrect speaker tags (SpeakerId) to avoid crosstalk.

Modify overly short timestamps to avoid excessively fast speech in dubbing.
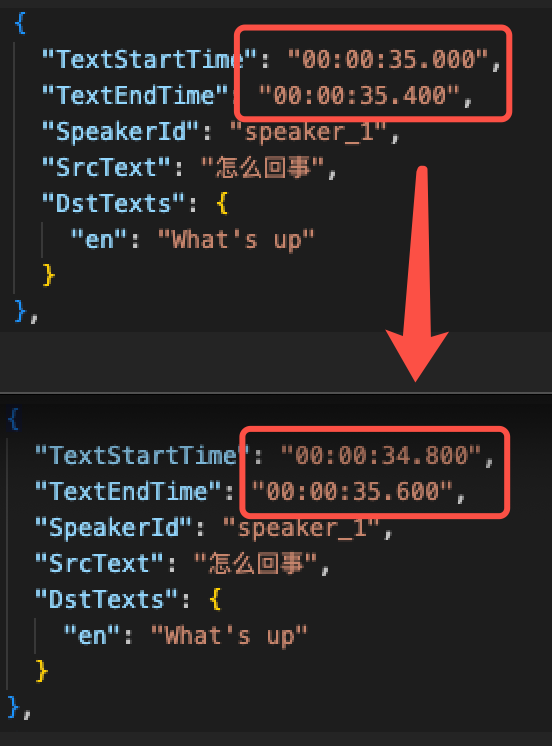
Modify the translation to make it more idiomatic and colloquial.
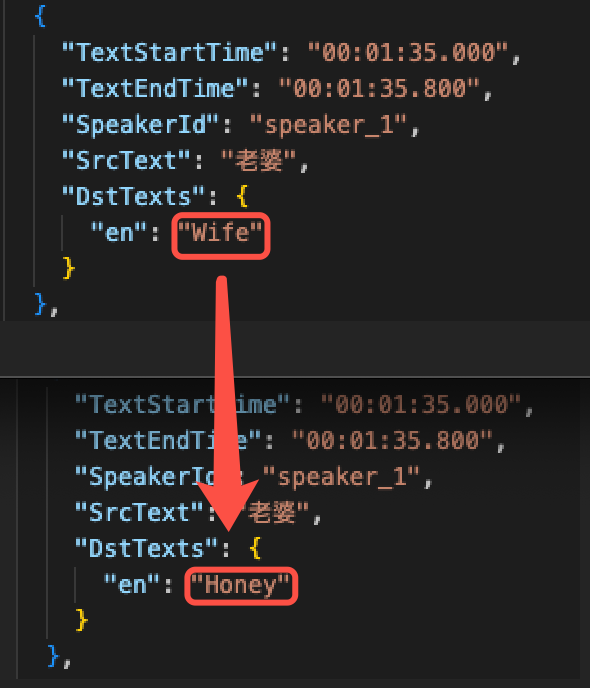
AI Dubbing Supported Languages
说明:
The AI dubbing feature uses cloned timbre by default.
The standard timbre capability is currently under upgrade and available only for beta testing. If you need to use the standard timbre, you can contact sales for support.
The following languages are supported when AI dubbing with cloned timbre is selected.
Language | Code | Supported as Source Language (SrcLang) | Supported as Target Language (DstLangs) |
Chinese | zh | ✓ | ✓ |
English | en | ✓ | ✓ |
Japanese | ja | ✓ | ✓ |
German | de | ✓ | ✓ |
French | fr | ✓ | ✓ |
Korean | ko | ✓ | ✓ |
Russian | ru | ✓ | ✓ |
Ukrainian | uk | ✓ | ✓ |
Portuguese | pt | ✓ | ✓ |
Italian | it | ✓ | ✓ |
Spanish | es | ✓ | ✓ |
Indonesian | id | ✓ | ✓ |
Dutch | nl | ✓ | ✓ |
Turkish | tr | ✓ | ✓ |
Filipino | fil | ✓ | ✓ |
Malay | ms | ✓ | ✓ |
Greek | el | ✓ | ✓ |
Finnish | fi | ✓ | ✓ |
Croatian | hr | ✓ | ✓ |
Slovak | sk | ✓ | ✓ |
Polish | pl | ✓ | ✓ |
Swedish | sv | ✓ | ✓ |
Hindi | hi | ✓ | ✓ |
Bulgarian | bg | ✓ | ✓ |
Romanian | ro | ✓ | ✓ |
Arabic | ar | ✓ | ✓ |
Czech | cs | ✓ | ✓ |
Danish | da | ✓ | ✓ |
Tamil | ta | ✓ | ✓ |
Hungarian | hun | ✓ | ✓ |
Vietnamese | vi | ✓ | ✓ |
Querying the Task Result
After an AI dubbing task is completed, two types of files are output and saved to the configured output path: the processed video file and the refined Speaker file. During dubbing, the translation in the original Speaker file is simplified to ensure a normal dubbing speed and prevent the speech from sounding too fast, thus generating a new Speaker file.
Querying the Result in the Console
1. You can check the task status on the Task Management page in the console. When the subtask status is Successful, click Callback JSON.
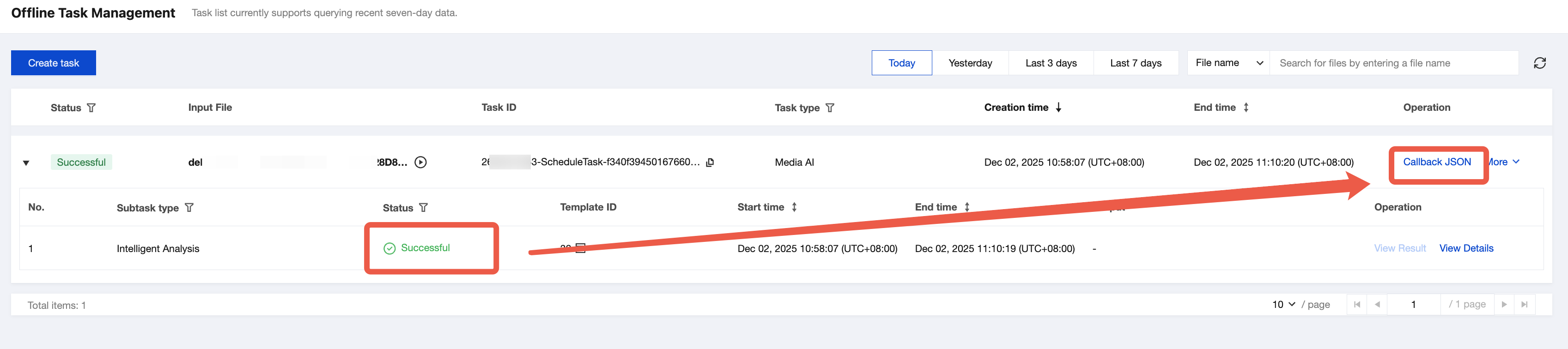
2. You can find the output file path in the output message.
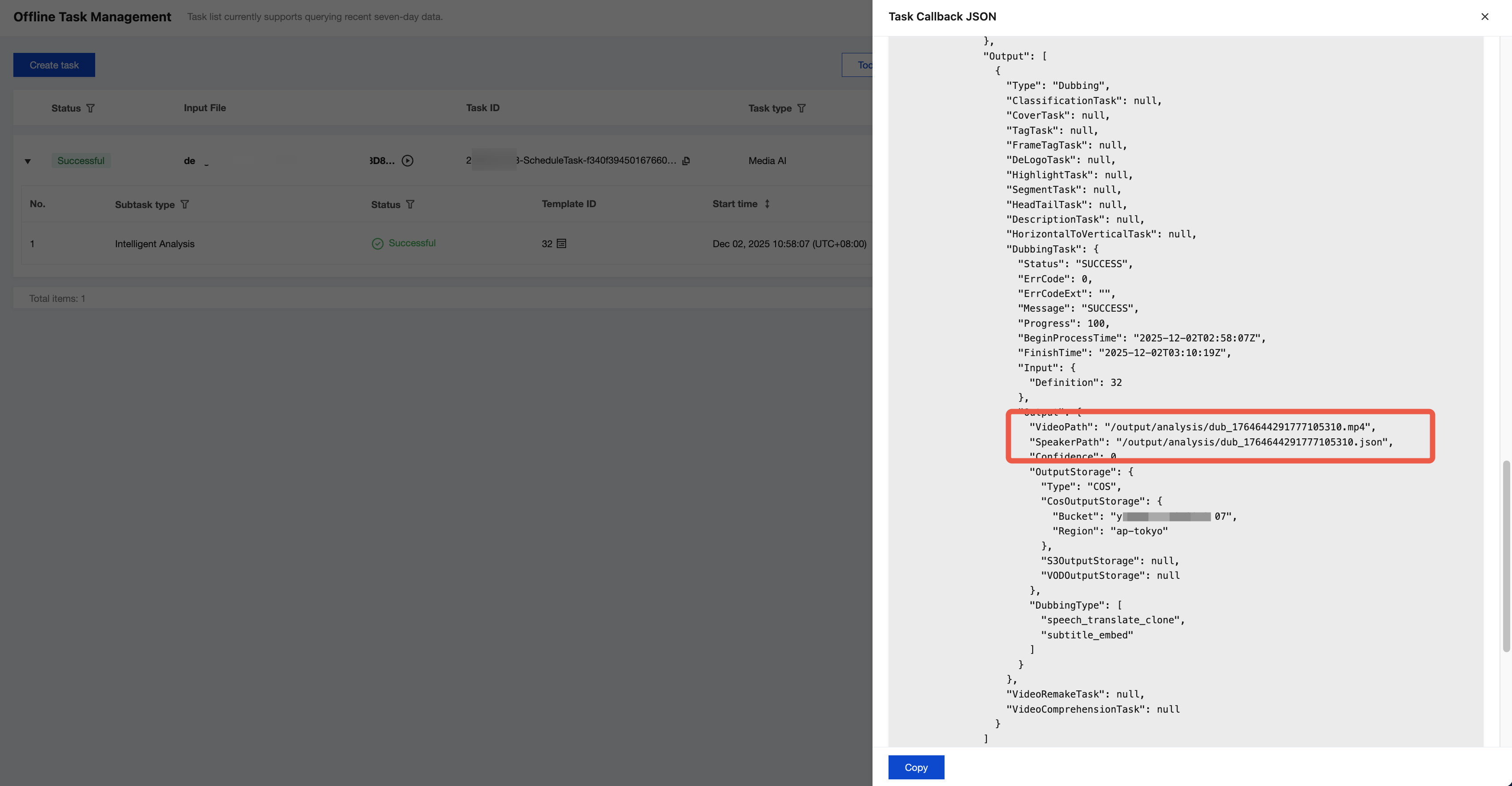
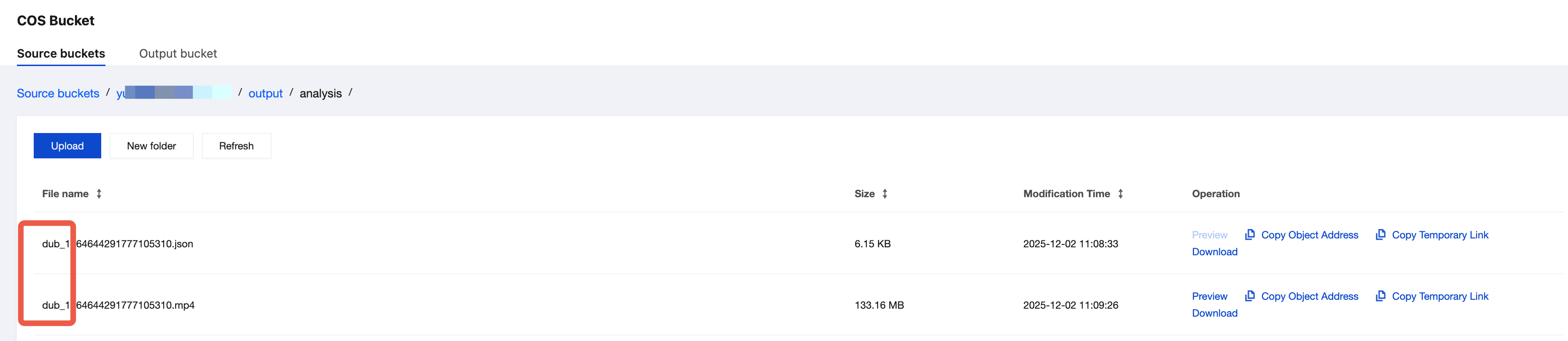
If COS is used as the output path, you can find the output file on the Orchestration Management > COS Bucket > Output Bucket page in the MPS console. The files with names similar to "dub-xxx.mp4" or "dub-xxx.json" are the processed video file and Speaker file generated after AI dubbing.
Event Notification Callback
When using ProcessMedia to initiate a media processing task, you can configure an event callback through the TaskNotifyConfig parameter. After the task processing is completed, the task result will be called back via the configured callback information. You can parse the event notification result through ParseNotification. The related data structure is listed below for reference.
Querying the Task Result by Calling an API
After ProcessMedia is used to initiate a media processing task, a task ID (TaskId) will be returned, such as 24000022-WorkflowTask-b20a8exxxxxxx1tt110253 and 24000022-ScheduleTask-774f101xxxxxxx1tt110253. Call the DescribeTaskDetail API and enter the task ID to obtain the task result. You need to parse the WorkflowTask ->AiAnalysisResultSet > DubbingTask > Output field to obtain the task result. The related data structure is listed below for reference.
Related Data Structure
FAQs
How Do I Obtain Clean Videos?
You can use the Smart Erase feature to remove subtitles and watermarks from videos to obtain clean videos.
Is It Supported to Input a Video and Perform One-Stop Processing, Including Subtitle Removal, Subtitle Translation, Subtitle Embedding, and AI Dubbing?
How Do I Generate a Speaker File from an SRT/VTT Subtitle File?
SRT or VTT subtitle files are supported. Usage examples:
Provide bilingual subtitle files (source-language and translated subtitles in one file).
python3 subtitle2speaker.py input.srt output.json --src_lang "zh" --dst_langs "en"
Provide two monolingual subtitle files (source-language and translated subtitles in separate files).
python3 subtitle2speaker.py input_src.vtt input_dst.vtt output.json --src_lang "zh" --dst_langs "en"
Note:
Speaker files generated from SRT/VTT subtitle files use a default Speaker ID for all speakers. You need to manually modify the Speaker information; otherwise, the dubbing effect may not meet expectations.